Frequently Asked Questions
Industry
What is a Passive Component?
A passive element is an electrical component that does not generate power but instead dissipates, stores and/or releases it. Passive components, like resistors, capacitors, and coil inductors, influence the flow of power and don’t need an external power source to function. Being passive, passive devices do not provide gain, amplification or directionality to a circuit but instead provide attenuation as they always have a gain less than one, unity. Therefore, passive devices cannot generate, oscillate, or amplify an electrical signal.
What is a Capacitor?
A capacitor is a fundamental passive electronic device designed to store electrical energy in an electric field. It accomplishes this by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced metalized surfaces, which are separated by a dielectric material. The dielectric material plays a crucial role in preventing direct contact between the metalized surfaces and influencing the capacitor’s performance. See Understanding Capacitors for more information.
What is a Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitor?
MLCC is a specific type of ceramic capacitor, which employs ceramic material as its dielectric. The manufacturing process involves layering ceramic material with alternating layers of metal contacts. This design enhances the capacitor’s performance and makes it suitable for various applications. See Understanding Capacitors for more information.
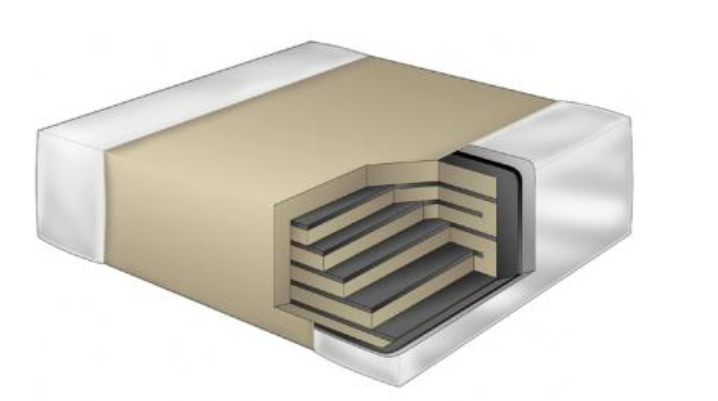
What’s the Difference between a SLC and a MLCC?
SLC’s are the most basic capacitor type, consisting of a single layer of dielectric material, or insulating layer, sandwiched between a positive and a negative electrode. An MLCC uses the principal capacitor design to build multiple layers of the same capacitor. MLCC is slightly thicker and an SLC but decreases the overall footprint.
What’s the difference between Thin Film & Thick Film?
The primary disparity between Thin Film and Thick Film products lies in the thickness of the resistive material. Thin Film components typically feature a resistive thickness of 0.1 micrometers (um) or smaller, while Thick Film components are significantly thicker, measuring in thousands of times the thickness of Thin Film. See Understanding Thin Film and Thick Film Products: A Comparative Guide for more information.
What is a Resistor?
A resistor is a two-terminal passive electrical component designed to control the flow of electric current within a circuit. Its primary function is to limit or regulate the current, leading to a controlled reduction in voltage across a specific section of the circuit. Understanding the role of resistors is essential in designing and optimizing electronic systems. See Understanding Resistors and Their Role in Circuits for more information.
What’s Ohm’s Law in Electrical Circuits?
Ohn’s Law stands as a fundamental principle in the realm of electrical circuits, providing a mathematical framework to comprehend the relationships between voltage, current, and resistance. Ohm’s Law is a fundamental formula that elucidates the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) within an electrical circuit. Formulated by German physicist Georg Simon Ohm, this law serves as a cornerstone for understanding and analyzing the behavior of electrical systems. See Understand Ohm for more information.
What does RoHS compliant mean?
Restriction of Hazardous Substances. RoHS is also known as Directive 2002/95/EC and referred to as the “lead-free” directive. Originating in 2003 by the European Union, this directive was established to limit the amount of hazardous chemicals in electronics in order to prevent the risks to human health and solve the problem of toxic electronic waste. Most of PPI components are RoHS compliant.
What happens if you put capacitors in parallel vs. in series?
By putting capacitors in parallel, the resulting circuit is able to store more energy since the equivalent capacitance is the sum of the individual capacitances of all capacitors involved. This can be used to better filter output signal and eliminate the AC ripple. There are some applications that require greater capacitance values than produced as a single capacitor. Using capacitors in parallel would be effective.
Capacitors, put together in series, will block store an equal amount of charge which means that the total amount of charge is evenly distributed across all of the capacitors.
What causes the “suck outs” in blocking capacitors?
“Suck outs” are caused by parallel resonances – the capacitor behaves like a series stub. For High-Q capacitors, the only way to do a better job is to use the vertical orientation to eliminate the lowest frequency PR. Broadband capacitors use loss to damp out the parallel resonances.
What’s the difference between a variable and fixed capacitor?
What is the recommended land pattern for the different Broadband series?
Our Broadband Application Note covers this in some detail, and a generally good practice is to choose the land width dimension about equal to that of the part. However, since an optimal land pattern depends on the customer’s particular substrate dielectric constant, thickness, and frequency range, PPI does not recommend a general-use land pattern. See https://passiveplus.com/resources/ for the Broadband Application Note.
What’s the difference between Class 1 and Class 2 dielectrics?
Class 1 dielectrics have the highest stable characteristics of frequency, voltage, time and temperature coefficients. Class 2
dielectrics offer higher dielectric constants but less stable properties. These capacitors are suited for decoupling and coupling applications where the capacitance value is not critical.
Passive Plus
What is the difference between the C and P series capacitors?
C is true NPO, P is a P90 (positive 90 PPM) characteristic. The C is a true NPO, +/- 30ppm. The P family has a +90ppm temperature characteristic.
What is the difference between C/P porcelain, and the N family?
C/P utilizes palladium electrodes, and magnesium titanate dielectric. The N family uses silver electrodes, and a more typical type of dielectric, suited for lower temperature firing. N has better Q’s at higher frequencies. The N-series is EIA standard case sizes (0201N, 0402N, etc.) while the C/P series is square (0505 = 50mils square).
What’s the general rule of thumb on the application frequencies where the lower conductive loss caps (the N series with silver electrodes) are superior in ESR to the lower dielectric loss caps (C/P series with palladium electrodes?
100-200MHz. The higher the capacitance, the lower the crossover frequency.
Why does PPI only offer 10nF and 100nF offerings for the Broadband family?
To address the entire market with cost effective product families.
Is there a 2225C or 3838C kit available for purchase?
Standard design kits are not available for this case size. PPI would create a custom kit of these larger capacitors according to customer’s requirements. Please contact PPI (sales@passiveplus.com) to inquire about a custom kit for our larger case size capacitors.
Are S-Parameters on the website?
The Scattering or S-parameter matrix describes networks with an arbitrary number of ports. It provides a relationship between the incident wave and the reflected and transmitted waves at each port over a range of frequencies. S-Parameters for PPI components can be found on the corresponding component page.
Are parts available through Digi-Key?
Some case sizes of PPI capacitors are available to purchase through Digi-Key. Availability is not guaranteed as Digi-Key may have limited quantities in stock. For deliveries on all PPI components, please contact PPI directly at sales@passiveplus.com.
Are sample kits available?
Standard Design Kits are available for the smaller case sizes. Case sizes offered are 0201N, 0402N, 0603N, 0805N, 1111N and 0505C/P and 1111C/P. Engineering Design Kits for the 0505C/P case size are available in magnetic and non-magnetic terminations. Most kits have 16 values, 10-pieces per value. Please see https://passiveplus.com/design-kits/ for more information about our kits.
What’s the difference between horizontal and vertical tape & reel?
Vertically-oriented components in tape & reel mean that the parts are vertically oriented in the tape so that the electrodes are perpendicular to the flat tape. Where horizontally-oriented components (standard orientation) mean that the capacitor’s electrode planes are parallel to the plane of the substrate or sits “flat” on the tape.
How does Tolerance affect lead time and Unit price for Traditional Hi-Q ‘C’, ‘P’ Caps?
Depending on the quantities required, a tight tolerance part may have a longer lead time. A tighter tolerance part will be more expensive than parts with looser tolerances.
What Capacitor case sizes and series do PPI carry?
Case Size |
Dimensions L x W inches(mm) |
PPI Product Series |
| 01005 | 0.016 x 0.008 (0.40 x 0.02) |
Broadband |
| 0201 | 0.024 x 0.012 (0.60 x 0.30) |
Broadband, EIA |
| 0402 | 0.049 x 0.020 (1.02 x 0.51) |
Broadband, EIA |
| 0505 | 0.55 x 0.55 (1.40 x 1.40) |
High-Q, X-Series |
| 0603 | 0.063 x 0.031 (1.57 x 0.81) |
Broadband, EIA |
| 0708 | 0.70 x 0.80 (1.65 x 2.02) |
EIA |
| 0805 | 0.080 x 0.50 (2.03 x 1.27) |
Broadband, EIA |
| 1111 | 0.11 x 0.11 (2.79 x 2.79) |
High-Q, EIA, X-Series |
| 2225 | 0.220 x 0.25 (5.72 x 6.25) |
High-Q, X-Series |
| 3838 | 0.380 x 0.380 (9.65 x 9.65) |
High-Q |
| 6040 | 0.600 x 0.400 (15.60 x 11.0) |
High-Q |
| 7676 | 0.760 x 0.760 (19.30 x 19.30) |
High-Q |
| 1313 | 1.35 x 1.35 (34.29 x 34.29) |
High-Q |
Does PPI have any parts with gold terminations?
PPI Broadband Capacitors are available in several terminations: Tin Plated over Nickel Barrier (RoHS Compliant), Tin/Lead (90%Sn/10%Pb), and Gold. Data sheets with further information can be found at https://passiveplus.com/products/fixed-capacitors/broadband-multilayer-capacitors/.
Can I get samples of the Broadband Capacitors?
PPI has a generous sampling policy. We offer our entire line of Broadband Capacitors on sample sheets with graphs specific to that particular lot, guaranteeing capacitor performance of the samples and giving the engineer exact performance data allowing them to determine which capacitor to incorporate into their project.
What components does PPI have that are non-magnetic for MRI applications?
PPI offers a large variety of non-magnetic components. The Non-Magnetic Component Brochure (https://passiveplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/PPI-NONMAGNETIC-COMPONENTS-BROCHURE-021924A.pdf) on our website provides comprehensive information about these components.
Are all PPI parts available on Tape & Reel?
Depending on the size and quantity required, PPI chip capacitors are available on Tape & Reel. Please be sure to mention your requirements upon requesting a quote as smaller quantities will be provided on cut tape.
What is the standard lead time for PPI components?
Lead time may vary depending on the parts specifications and quantities required. Contact PPI for exact delivery dates.
What is the best way to get a hold of PPI?
PPI headquarters is located in New York (USA). Emails are generally the best way to contact PPI and will be replied to within 24 hours of receipt. Emails can be sent to a specific person or through our website where inquiries will be directed to the appropriate team.
If I’m unsure of which PPI component that best suits my project, is there someone at PPI who can assist me?
Yes, feel free to reach out to sales@passivplus.com with your contact information and questions, and someone will address your email with suggestions.
Is PPI able to cross competitor part numbers?
Yes, our team has extensive experience with crossing our competitors’ part numbers and will be happy to provide you with crosses for their components. Quick Cross Reference charts are available on our website https://passiveplus.com/resources/cross-reference-charts/
How long will it take to get a quote?
You will receive a response to your inquiry within 24 hours after receipt.
Are all of PPI’s Thin Film Components custom parts?
All thin film components, except for the standard High Frequency resistors, are made to order.
Where are PPI components manufactured?
Depending on the case size, PPI ceramic capacitors are manufactured either in China or the USA. Our Broadband capacitors are manufactured in the USA. Our Trimmer Capacitors are manufactured in Europe. Our Thin Film components are manufactured in the USA.
Will PPI perform specific testing if a customer requested?
Please contact PPI with requirements and our team will look into the possibility of performing testing.
Is PPI ISO certified?
Yes, PPI is ISO 9001:2015 certified. This means PPI Quality Product and Delivery meets and/or exceeds Customer Requirements while providing excellent customer service through our Quality Management Systems.
Does PPI perform Hi-Rel screening on their parts?
PPI offers Hi Reliability screening for the MLCC in production (at no extra charge). 100% Automated Sonoscan is done on all larger case sizes, increasing reliability by screening out electrically undetectable internal defects. 100% High Voltage Partial Discharge testing is performed on all leaded 2225 and larger case size capacitors. This testing detects faint electrical discharges in multilayer ceramic capacitors under High Voltage conditions. 100hour burn in is also performed on all leaded 1111 and larger case seize capacitors and assemblies ensuring reliability. The PPI burn-in is done at extended voltage and 125°C, with Capacitance, Dissipation Factor (inverse of Q), and IR (Insulation Resistance) measurements taken before and after burn in.
Does PPI have a soldering guide to help with hand soldering?
Yes, PPI has written a comprehensive guide and is found on our website https://passiveplus.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/PPI-Soldering-Guide-071521A.pdf
PPI Academy
Unlock your engineering potential with PPI Academy's comprehensive educational resources – start exploring today!
